Wholesale Payments – a Guide to the Benefits and Drawbacks
The Evolution of B2B Wholesale Payments
In the last years, the B2B wholesale payment landscape experienced a significant shift towards digitalization and automation. A few key observations from the past years include:
- Digital Transformation: In 2023, the B2B payments market, valued at around $240 trillion, began moving away from traditional methods like checks in favor of digital solutions. This change aimed to enhance efficiency, reduce fraud, and lower costs.
- Increase in Digital Transactions: The year saw a significant rise in the volume and size of digital transactions. A trend emerged where a growing number of B2B buyers were comfortable making large-scale digital purchases, sometimes exceeding half a million dollars.
- Growth of Embedded Payments: The embedded payments industry showed impressive growth, projected to expand from $43 billion in 2021 to $138 billion by 2026, indicating a deepening integration of payment systems into broader business operations.
Looking into the future, the B2B wholesale payment sector is expected to continue its trajectory towards more innovative, efficient, and secure payment methods. The focus is likely to be on further enhancing digital transaction capabilities and expanding the reach of tech-driven payment solutions, aligning with the broader digital transformation trends in the business world.
In 2023, the B2B payments market, valued at around $240 trillion, began moving away from traditional methods like checks in favor of digital solutions. This change aimed to enhance efficiency, reduce fraud, and lower costs.
Wholesale Payments
Understanding the nuances of wholesale and B2B payments is crucial, especially when compared to B2C transactions. Wholesale transactions are typically larger, involve bulk purchases, and often include differentiated pricing and payment terms. Unlike B2C, where customers pay at the point of sale, B2B and wholesale customers frequently have payment terms that allow for later payment, fostering a trust-based relationship.
Wholesale and B2B Payments vs. B2C Payments
Understanding the Difference Between Wholesale and B2B Payments Compared to B2C
Understanding the differences between wholesale and B2B payments is very important, and it starts with identifying their fundamental differences from typical B2C transactions.
Volume and Scale: One of the most significant differences lies in the scale of transactions. Wholesale customers typically purchase in bulk, acquiring multiple units of a product, as opposed to individual consumers who buy items for personal use. This larger scale naturally leads to more substantial transaction values in the wholesale sector.
Complexity and Customization: Additionally, wholesale transactions tend to be more intricate than standard retail purchases. It’s common in the wholesale world for brands to offer custom pricing and payment terms, tailored to each customer based on individual agreements and negotiations. This level of customization adds layers of complexity to B2B transactions.
Payment Terms: Another key distinction is in the payment structure. Unlike B2C transactions, where payment is usually made at the point of sale, B2B and wholesale transactions often involve deferred payment terms. This practice, rooted in the repetitive and trust-based nature of B2B relationships, allows wholesale customers to pay at a later date.
Understanding these core differences sets the stage for diving into the various methods of payment in wholesale, each with its own set of considerations and implications for businesses.
Different Methods of Wholesale Payments
In the traditional B2B wholesale payments, we see three types:
- Invoice Payments: The traditional method where payments are made post-delivery, based on issued invoices.
- Credit Card Payments: Business credit cards are used for transactions, providing convenience and potential rewards.
- Checks: Once a staple, now less common due to slower processing, but still used in certain sectors.
However, the landscape of B2B wholesale payments is evolving. Here are some additional methods gaining traction in the digital B2B wholesale payments world:
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT): Including direct bank transfers and ACH payments, known for efficiency and lower fees.
- Online Payment Gateways: Like PayPal, Stripe, or Square, facilitating secure online transactions.
- Mobile Payment Solutions: Services such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, offering fast and secure transactions.
- Cryptocurrency Payments: Digital currencies providing benefits like lower transaction fees and enhanced security.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Services: Allowing deferred payments to improve buyer cash flow.
- Wire Transfers: Used for larger sums, especially in international trade.
- Purchase Orders (PO): Formal agreements for buying goods or services at agreed prices.
- Trade Credit: Where buyers purchase on account and pay the supplier later.
- Digital Wallets: Storing payment information for quick transactions.
Each of these methods has its benefits and drawbacks that we will go into detail with below.
1. Invoice Payments
In B2B transactions, invoice payments are evolving with digital trends. The average cost to process a supplier payment is about $8, primarily due to labor costs. The global B2B payments market, valued at approximately $240 trillion, is experiencing growth, partly driven by the rise of digital commerce in the B2B sector. This shift towards digital solutions aims to reduce costs, minimize errors, and combat fraud associated with traditional invoice processing.
- Benefits:
- Allows customers a credit period, aiding in cash flow management.
- Convenient for customers, potentially leading to larger and more frequent orders.
- Usually incurs low or no transaction costs.
- Drawbacks:
- Risk of late or non-payment; according to PayStand, 47% of B2B invoices are paid late.
- Can negatively impact the seller’s cash flow; the average B2B payment cycle is 35 days.
2. Credit Card Payments
Credit card usage in B2B transactions, particularly in retail and small business sectors, is witnessing growth. The convenience and immediacy of credit card payments are key factors driving their increased adoption. However, businesses remain mindful of the associated transaction fees. In the United States, credit card ownership saw a significant rise, with 84% of adults possessing a credit card in 2021, indicating their integral role in financial transactions. By the end of 2022, the number of credit card users in the U.S. reached 166 million, a notable increase from previous years. This trend reflects the growing reliance on and acceptance of credit cards, not just in personal finance but also in business transactions.
- Benefits:
- Immediate payment, improving the seller’s cash flow.
- Convenient and familiar to many customers.
- Can offer rewards or cashback benefits.
- Drawbacks:
- Transaction fees ranging from 1.5% to 4% can be significant on large orders.
- Spending limits on cards may hinder large transactions.
3. Checks
Checks, although declining, are still used in about 40% of U.S. B2B transactions as of 2022. Their ongoing usage is attributed to familiarity and established processes. However, the trend is shifting, with a notable decrease to 33% in North American B2B transactions, as companies increasingly move towards electronic payments for efficiency and cost savings.
- Benefits:
- Preferred by some businesses due to familiarity.
- Typically, low or no transaction fees.
- Drawbacks:
- Time-consuming process with manual handling.
- Risk of errors, fraud, and bounced checks.
4. Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
EFTs, including direct bank transfers and Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments, are increasingly utilized in various industries due to their efficiency. The preference for EFT in B2B transactions is growing as businesses seek faster, more cost-effective payment solutions. This trend is part of a broader move towards digitalization in financial transactions, reflecting the need for quicker and more streamlined payment processes in the business world.
- Benefits:
- Efficient and fast, especially for large sums.
- Lower transaction fees compared to other methods.
- Drawbacks:
- Requires banking information exchange, which might not be preferred by all customers.
- May not be suitable for small or infrequent transactions.
5. Online Payment Gateways
Online payment gateways, initially popular in e-commerce, are increasingly being adopted in B2B sectors like technology and international trade. The B2B digital payment market, which includes online payment gateways, has shown significant growth. It’s projected to expand from $4.2 billion in 2023 to $8.2 billion by 2028, demonstrating the rising importance of these gateways in business transactions. This growth is indicative of their popularity due to factors like security, convenience, and the rapid expansion of e-commerce, which increasingly demands such digital payment solutions.
- Benefits:
- Secure and convenient for both parties.
- Facilitates international transactions.
- Drawbacks:
- May involve transaction fees.
- Some businesses may prefer traditional payment methods.
6. Mobile Payment Solutions
Increasingly popular in consumer markets, mobile payment solutions are rapidly gaining traction in the B2B sector, particularly in technologically advanced industries. These solutions offer speed and convenience, aligning well with the growing trend of mobile commerce. The U.S. mobile payment market, which was valued at $53.5 billion in 2022, is expected to grow exponentially, reaching over $607.9 billion by 2030. This remarkable growth underscores the potential impact and scalability of mobile payment technologies in the B2B landscape.
- Benefits:
- Quick and easy, ideal for on-the-go transactions.
- Enhanced security features.
- Drawbacks:
- May not be universally adopted by all B2B customers.
- Reliant on mobile technology infrastructure.
7. Cryptocurrency Payments
Cryptocurrency payments are carving out a niche in the B2B landscape, particularly appealing in sectors like technology, international trade, and for businesses prioritizing privacy. While their usage is on the rise, it’s influenced by regulatory environments and the varying degrees of market familiarity with cryptocurrencies. Notably, international B2B blockchain transactions are anticipated to reach a significant milestone, with projections suggesting they could top $1.7 billion by 2025. This forecast reflects the growing interest and potential of cryptocurrency as a viable, secure option for B2B transactions on a global scale.
- Benefits:
- Lower transaction fees and fast international transfers.
- Enhanced security and privacy.
- Drawbacks:
- Volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
- Limited adoption and understanding in the B2B sector.
8. Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Services
BNPL is growing in the B2B sector, particularly in retail and wholesale. The U.S. BNPL lending market will grow from $156.58 billion in 2023 to $232.23 billion in 2024, reflecting its increasing popularity in business transactions. This growth signifies the rising adoption of flexible payment options in the B2B space.
- Benefits:
- Improves buyers’ cash flow by deferring payments.
- Can attract customers seeking flexible payment options.
- Drawbacks:
- Risk of non-payment or late payment.
- May involve fees or interest for the buyer.
9. Wire Transfers
Wire transfers, particularly for large or international payments, are still commonly used in B2B transactions. In 2022, businesses reported conducting between 100 to 499 wire transfers monthly. While they remain vital for high-value transactions, wire transfers are facing competition from more cost-effective digital payment methods.
- Benefits:
- Ideal for large, international transactions.
- Secure and reliable.
- Drawbacks:
- Can involve higher fees, especially for international transfers.
- Not as fast as EFT for domestic transactions.
10. Purchase Orders (PO)
Still prevalent, but in 2023, digital systems began replacing traditional paper-based Purchase Orders (POs) in sectors like manufacturing and government contracting. This change reflects a broader trend toward efficiency and modernization in procurement processes.
- Benefits:
- Formalizes transaction terms and provides legal protection.
- Useful for regular and bulk orders.
- Drawbacks:
- Administrative overhead in managing and processing POs.
- May slow down the ordering process.
11. Trade Credit
Trade credit remains a critical component in B2B transactions, especially in sectors like wholesale, manufacturing, and construction. In 2023, the trend in the U.S. showed an increased focus on stricter trade credit policies due to heightened payment risks. The Atradius Payment Practices Barometer survey reported that 55% of B2B invoiced sales were overdue, and bad debts affected 9% of credit-based B2B sales. These trends highlight the evolving nature of trade credit in the face of economic challenges and the necessity for effective credit management strategies.
- Benefits:
- Strengthens buyer-seller relationships.
- Encourages repeat business.
- Drawbacks:
- Risk of delayed payments affecting cash flow.
- Requires careful management to avoid bad debts.
12. Digital Wallets
Digital wallets are increasingly embraced in the B2B landscape. In 2023, the U.S. mobile payment market was valued at $53.5 billion and is projected to reach over $607 billion by 2030. This surge is indicative of the growing preference for digital wallets, known for their speed and convenience. Despite their origin in B2C, digital wallets are gaining momentum in B2B sectors like technology and retail, reflecting a broader shift towards more versatile and secure payment options in business transactions.
- Benefits:
- Convenient and fast for digital-savvy customers.
- Reduces need for physical card or cash handling.
- Drawbacks:
- May not be preferred by all business customers.
- Reliant on internet access and digital infrastructure.
What Type of Wholesale Payments Should You Use?
Choosing the Right Wholesale Payment Method
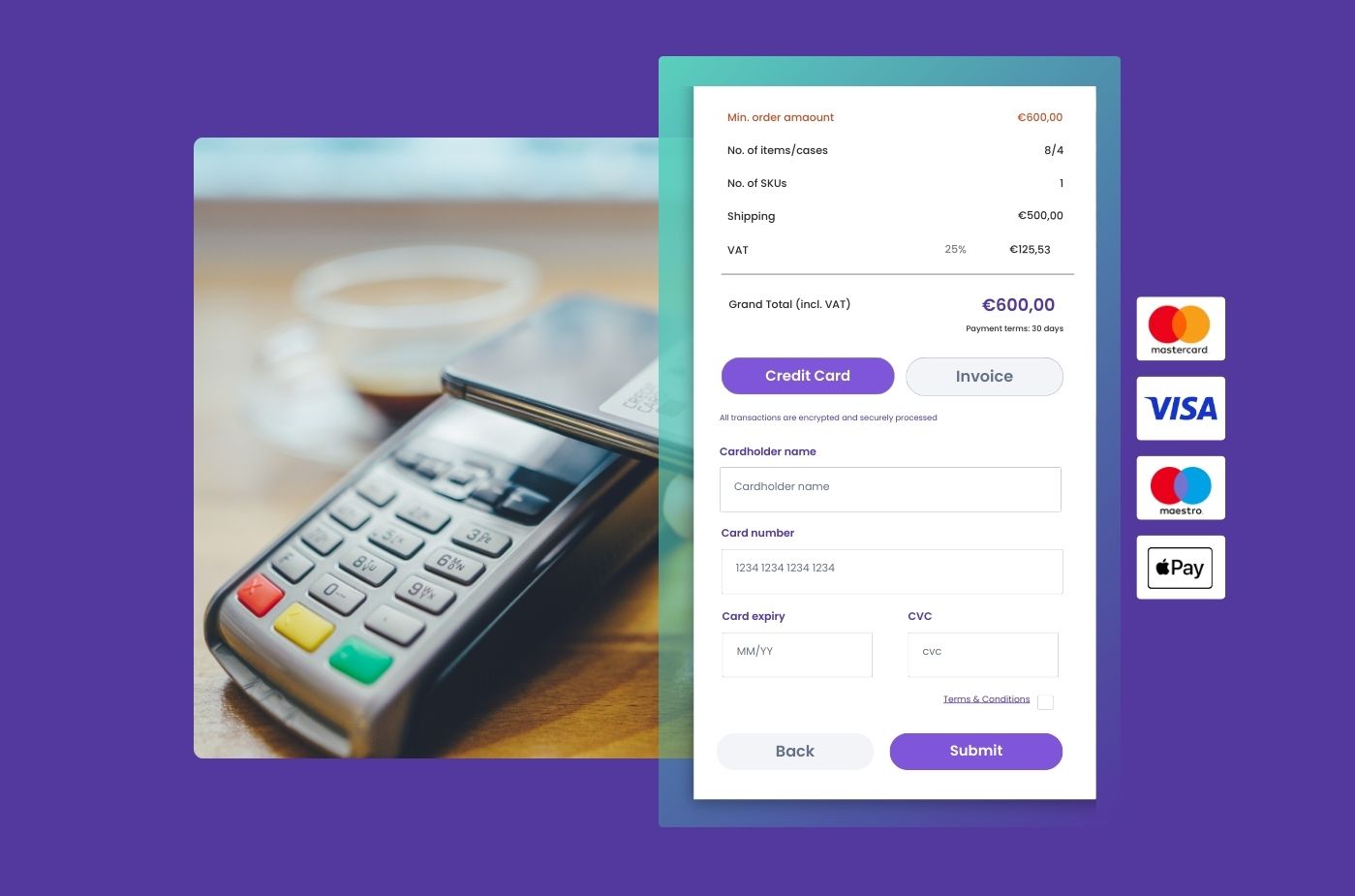
Picking the right payment method for your wholesale business involves more than just preference. It’s a strategic choice that can influence your overall operations. Factors like your industry, company size, and the way you interact with customers can all play a part. Often, your customers will have their own preferences that you’ll need to accommodate.
Adding multiple payment options can make things easier for your customers and may even boost your sales, as flexibility in payments is highly valued. Also, incorporating a reliable B2B eCommerce payment system can streamline the whole process, making transactions smoother and more secure.
By understanding these key points and choosing a payment system that integrates well with your B2B platform, you can make smarter decisions that benefit everyone involved. This approach not only makes paying easier but also helps keep your business competitive and customer-friendly.